Dopamine is a crucial neurotransmitter in the brain that plays a vital role in regulating mood, motivation, and reward. Often referred to as the “feel-good” chemical, dopamine influences many aspects of human behavior and physiological functioning.
Click here to see a short video : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QmOF0crdyRU
What is Dopamine?
Is a type of neurotransmitter, a chemical messenger that transmits signals between nerve cells (neurons) in the brain. It is produced in several areas of the brain, including the substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area (VTA).
It is an important chemical messenger in your brain that has many functions. It’s involved in reward, motivation, memory,
attention, and even regulation of body movements. When dopamine is released in large amounts, it creates feelings of
pleasure and reward, which motivate you to repeat a specific behavior.
The levels are typically well-regulated within the nervous system. Moreover if these levels get dysregulated, you may develop a
mood disorder like depression
Functions of Dopamine
Dopamine is involved in several key brain functions:
- Reward and Pleasure: is most famously known for its role in the brain’s reward system. If It is released during
pleasurable activities, such as eating, sex, and social interactions, reinforcing behaviors that are essential
for survival and well-being.
- Motivation and Drive: It motivates us to pursue goals and rewards. High levels of can enhance focus and drive,
making tasks feel more rewarding.
- Motor Control: It is critical for coordinating smooth and purposeful movements. This is why dopamine deficiency is
a hallmark of Parkinson’s disease, which leads to motor impairments.
- Cognition and Attention: affects cognitive functions, including attention, learning, and memory. It helps
regulate information flow in the brain, impacting how we process and respond to stimuli.
The Dopamine Pathways
There are several key pathways in the brain:
Mesolimbic Pathway: Often referred to as the reward pathway, it is involved in the sensation of pleasure and reinforcement of rewarding behaviors.
Mesocortical Pathway: This pathway influences cognitive control, motivation, and emotional responses.
Nigrostriatal Pathway: Involved in motor control and coordination. Dysfunction in this pathway is associated with Parkinson’s disease.
Tuberoinfundibular Pathway: Regulates the release of hormones, including those involved in stress response and reproductive functions.
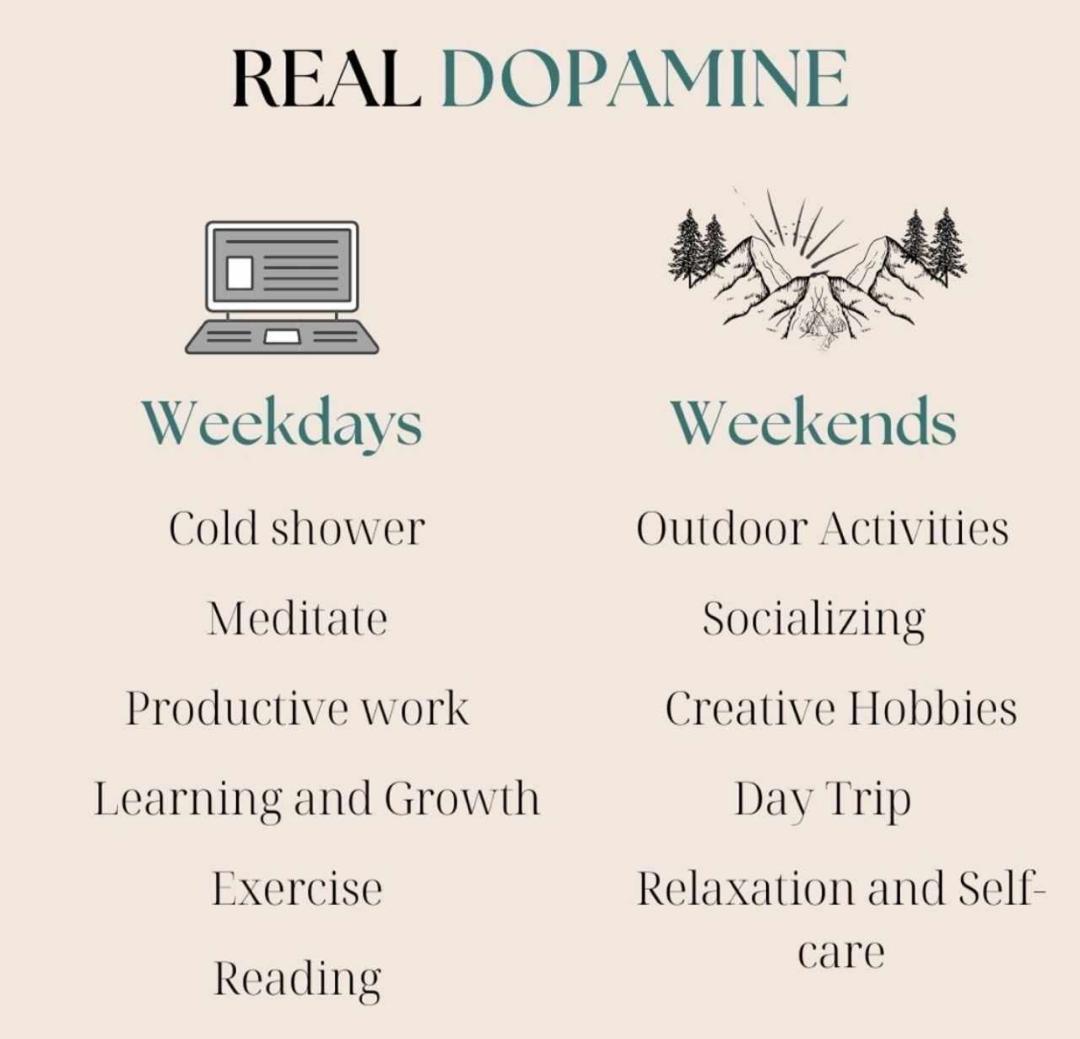
There are several ways to boost dopamine levels naturally:
Exercise: Regular physical activity increases the production and receptor sensitivity in the brain.
Diet: Consuming foods rich in tyrosine, an amino acid that is a precursor to dopamine, can help. Foods such as almonds,
bananas, avocados, and lean proteins are beneficial.
Sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining dopamine levels. Sleep deprivation can reduce dopamine receptors
in the brain.
Meditation and Mindfulness: Practices that reduce stress and enhance well-being can positively influence dopamine levels.
Hobbies and Activities: Engaging in activities that bring joy and satisfaction can naturally boost the mental health.
In Addition 10 Natural Ways to Raise Your Dopamine
- Eats lots of Protein
- Eat less saturated fats
- Consume Probiotics
- Eat Velvet Beans
- Exercise Often
- Get Enough Sleep
- Listen to Music
- Mediate
- Get Enough Sunlight
- Consider Supplement
Frequently asked questions
What are the symptoms of low dopamine?
Not having enough can negatively affect your mood, focus, coordination, motivation, and enthusiasm for
things that normally bring you joy. In extremely rare cases, a child may develop the deficiency syndrome, a progressive
movement disorder.
What triggers dopamine release?
Anything that gives you pleasure will trigger the release of dopamine. This can range from a fun activity you enjoy, like
dancing or cooking, to sex, shopping, and even certain drugs. It activates the reward pathway in the brain, leading
you to desire these activities more. For this reason, it can play a role in addiction.
Is ADHD a lack of dopamine?
Moreover while researchers haven’t determined what causes ADHD, they have found that people living with ADHD
have different levels than neurotypical people. Learn more about research on the role of dopamine in ADHD.
Which foods increase dopamine the most?
Suggested foods include nuts, berries, certain leafy vegetables, foods that contain Omega-3 like fish, and other nutrient-dense foods. Learn more about the Parkinson’s diet.
Dopamine is a powerful neurotransmitter that significantly impacts our emotional and physical well-being. Understanding its functions and how it affects our behavior can help us make informed choices to maintain a healthy balance in our lives.
Whether through lifestyle changes or medical interventions, managing the levels is crucial for mental and physical health.
Read Also: https://placesandlifestyle.com/achieving-holistic-health-and-wellness/