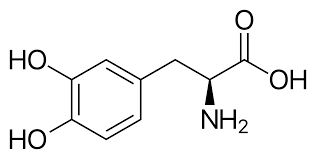
Levodopa, often referred to as L-DOPA, is a crucial medication in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. As a precursor to dopamine, levodopa plays a significant role in managing the symptoms of this neurodegenerative disorder.
l-DOPA, l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, is made and used as part of the normal biology of some plants and animals, including humans. Humans, as well as a portion of the other animals that utilize l-DOPA, make it via biosynthesis from the amino acid l-tyrosine.
What is Levodopa?
Levodopa is an amino acid that the body converts into dopamine, a neurotransmitter that is essential for controlling movement and coordination. Parkinson’s disease is characterized by the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, leading to symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination.
Once administered, levodopa crosses the blood-brain barrier and is then converted to dopamine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase. This increase in dopamine levels in the brain helps to alleviate the motor symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease.
Myths and Facts about Levodopa: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QyBGAuhBYzA
Levodopa is often prescribed in combination with carbidopa, a medication that inhibits the peripheral metabolism of levodopa. Carbidopa ensures that more levodopa reaches the brain before being converted into dopamine. This combination allows for lower doses of levodopa, reducing side effects such as nausea and cardiovascular issues.
Benefits of Levodopa
Symptom Relief: has highly effective in reducing the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Patients often experience significant improvements in mobility and quality of life.
Proven Track Record: has been the gold standard treatment for Parkinson’s disease for decades, with extensive clinical evidence supporting its efficacy.
Despite its benefits, it can have side effects, particularly with long-term use. These may include:
Dyskinesias: Involuntary, erratic movements that can occur with prolonged use.
Motor Fluctuations: Variations in the effectiveness of the medication, leading to periods of improved and worsened symptoms.
Nausea and Vomiting: Common initial side effects that can be mitigated with carbidopa.
Orthostatic Hypotension: A drop in blood pressure upon standing, which can cause dizziness and fainting.
Levodopa’s journey begins upon ingestion, where it travels through the digestive system and crosses the blood-brain barrier. Once in the brain, it is converted into dopamine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase. This process replenishes the depleted dopamine levels, helping to restore normal motor function.
Protein intake can affect the absorption of levodopa, as dietary amino acids compete with the drug for transport across the gut and blood-brain barrier. Patients are often advised to manage their protein consumption and possibly take on an empty stomach or with a light, low-protein snack.
Future of Levodopa Therapy
Ongoing research aims to improve the delivery and efficacy of levodopa. Advances in formulation, such as extended-release
versions and infusion pumps, seek to provide more stable symptom control. Additionally, there is ongoing exploration into
neuroprotective strategies that could slow the progression of Parkinson’s disease, potentially enhancing the long-term benefits.
Extended-release Formulations: Designed to provide more stable blood levels of the drug, reducing motor fluctuations.
Infusion Pumps: Deliver continuous levodopa, maintaining steady dopamine levels.
Neuroprotective Strategies: Research into ways to slow the progression of Parkinson’s disease may enhance the long-term benefits of levodopa.
In Conclusion: A Steady Flight Path
Much like a co-pilot ensures the flight’s success, carbidopa is often paired with to enhance its efficacy. Carbidopa inhibits the enzyme that breaks down levodopa before it reaches the brain. This means more of it can cross the blood-brain barrier, increasing its availability and effectiveness while reducing peripheral side effects like nausea and vomiting.
Levodopa has charted a successful course in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, much like a reliable aircraft on a well-planned flight path. While it has its challenges, the benefits of improved motor control and quality of life make it an indispensable part of Parkinson’s therapy. Ongoing innovations promise to enhance its effectiveness, ensuring that levodopa remains at the forefront of managing this complex condition, guiding patients towards a smoother journey through life.
Read Also: https://placesandlifestyle.com/dopamine/